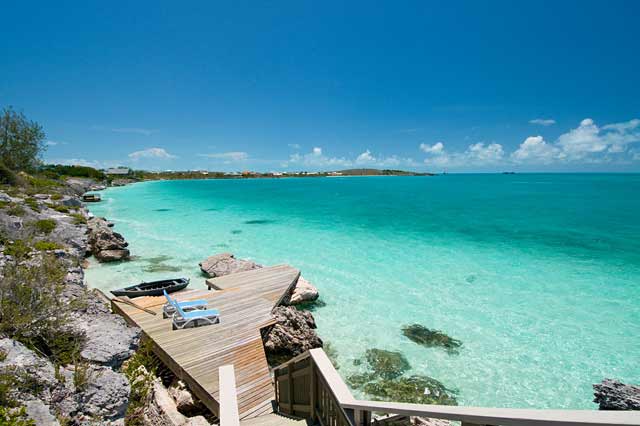
The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union consisting of two groups of tropical islands in the Caribbean, the larger Caicos Islands and the smaller Turks Islands, known for tourism and as an offshore financial centre.
The Turks and Caicos Islands lie southeast of Mayaguana in the Bahamas island chain and north of the island of Hispaniola. Cockburn Town, the capital since 1766, is situated on Grand Turk Island about 1,042 kilometres (647 mi) east-southeast of Miami in the United States. The islands have a total land area of 430 square kilometres .The islands are geographically contiguous to the Bahamas, but are politically a separate entity.
The Turks and Caicos Islands are named after the Turk's-cap cactus (Melocactus communis), and the Lucayan term "caya hico", meaning string of islands. The first inhabitants of the islands were Arawakan-speaking Taíno people who crossed over from Hispaniola sometime from 500 to 800. Together with Tainos who crossed over from Cuba to the southern Bahamas around the same time, these people became the Lucayans. Around 1200 the Turks and Caicos Islands were resettled by Classical Taínos from Hispaniola. Soon after they arrived in the islands in 1492, the Spanish began capturing the Taínos of the Turks and Caicos Islands and the Lucayans as slaves to replace the largely depleted native population of Hispaniola. The southern Bahama Islands, including the Turks and Caicos Islands, were completely depopulated by about 1513, and remained so until the 17th century.
The Turks and Caicos Islands lie southeast of Mayaguana in the Bahamas island chain and north of the island of Hispaniola. Cockburn Town, the capital since 1766, is situated on Grand Turk Island about 1,042 kilometres (647 mi) east-southeast of Miami in the United States. The islands have a total land area of 430 square kilometres .The islands are geographically contiguous to the Bahamas, but are politically a separate entity.
The Turks and Caicos Islands are named after the Turk's-cap cactus (Melocactus communis), and the Lucayan term "caya hico", meaning string of islands. The first inhabitants of the islands were Arawakan-speaking Taíno people who crossed over from Hispaniola sometime from 500 to 800. Together with Tainos who crossed over from Cuba to the southern Bahamas around the same time, these people became the Lucayans. Around 1200 the Turks and Caicos Islands were resettled by Classical Taínos from Hispaniola. Soon after they arrived in the islands in 1492, the Spanish began capturing the Taínos of the Turks and Caicos Islands and the Lucayans as slaves to replace the largely depleted native population of Hispaniola. The southern Bahama Islands, including the Turks and Caicos Islands, were completely depopulated by about 1513, and remained so until the 17th century.
The first documented European to sight the islands was Spanish conquistador Juan Ponce de León, who did so in 1512. During the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries, the islands passed from Spanish, to French, to British control, but none of the three powers ever established any settlements.
For several decades around the turn of the 18th century they became popular pirate hideouts. Bermudian salt collectors settled the Turk Islands around 1680. In 1765–1783 they were under French occupation and again after the French captured the archipelago in 1783. After the American Revolution (1775–1783) many loyalists fled to Caribbean colonies, including (in 1783) the first settlers on the Caicos Islands; cotton became an important crop briefly. In 1799, both the Turks and the Caicos island groups were annexed by Britain as part of the Bahamas.









No comments:
Post a Comment
Love to hear your thoughts!